The rise of quantum computing has raised concerns about the security of Bitcoin. In its current state, Bitcoin’s cryptography may not be secure enough to withstand attacks from quantum computers.
This could potentially lead to hackers stealing money from Bitcoin wallets. So, should you be concerned?
What exactly makes a Computer, Quantum?
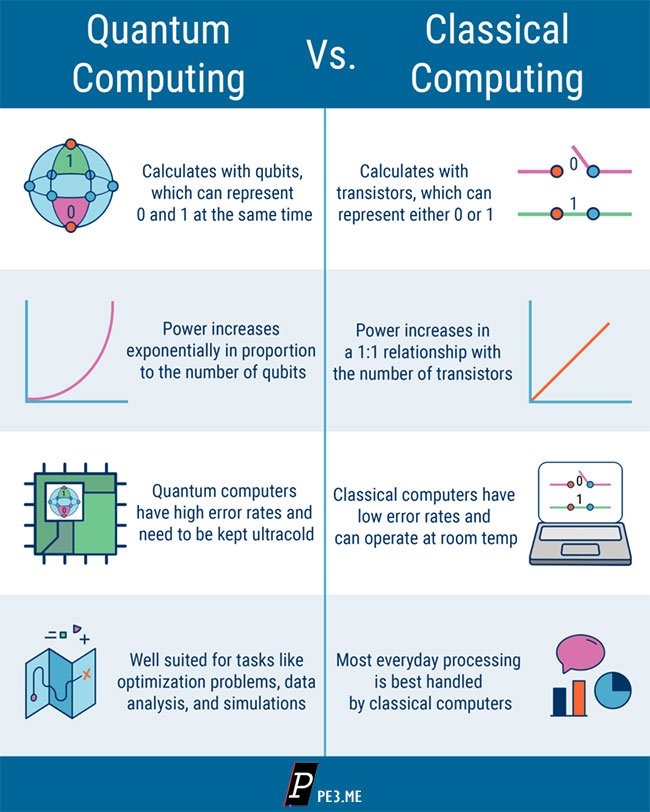
A quantum computer is a type of computer that uses quantum mechanics to store and process information.
Unlike traditional computers that use bits, which can only be either a 0 or a 1, quantum computers use qubits, which can be both 0 and 1 at the same time.
Think of it like a light switch in a room. A traditional computer is like a light switch that can only be either on or off, while a quantum computer is like a dimmer switch that can be both on and off at the same time. This allows the quantum computer to explore multiple possibilities at once and find the best solution much faster.

Quantum computing isn’t currently in a useable state for general use, but it is getting closer to be in a position to perform specific tasks, like cracking encryption.
In fact, a group of researchers has claimed that quantum computers can now crack the encryption we use to protect emails, bank accounts, and other sensitive data.
A group of researchers has claimed that quantum computers can now crack the encryption we use to protect emails, bank accounts and other sensitive data. Although this has long been a theoretical possibility, existing quantum computers weren’t yet thought to be powerful enough to threaten encryption. – New Scientist
Quantum Computing, Blockchain and Bitcoin
Quantum computing is a threat to blockchain technology. Blockchain is the underlying technology that powers cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum and Litecoin. It’s also used in other applications like supply chain management and even healthcare records storage.
A quantum computer could potentially crack a bitcoin wallet address by using its ability to perform calculations faster than traditional computers. Bitcoin wallet addresses are protected by a complex mathematical problem called a cryptographic hash function. This function is designed to be difficult to reverse engineer, which means that it should be nearly impossible to determine the input (the private key) that generated a specific output (the public address) of the hash function.
However, quantum computers can use a special algorithm called Shor’s algorithm to solve this problem much faster than a traditional computer. Shor’s algorithm can factor large numbers into their prime factors, which is useful for cracking the cryptographic hash function used by bitcoin wallet addresses.
If a quantum computer were to successfully crack the hash function of a bitcoin wallet address, it could potentially access the wallet and steal the bitcoins stored in it.
The Future of Quantum Computing and Bitcoin
While the threat of quantum computing to Bitcoin is certainly real, it’s not necessarily imminent. A lot of research and development needs to be done before we see any significant impact on the cryptocurrency market. And even then, there are many potential solutions that could prevent quantum computers from breaking Bitcoin’s cryptography such as:
Using post-quantum cryptography (such as elliptic curve cryptography) or lattice-based cryptography or;
moving from SHA256 to SHA3 or Keccak256, which are both resistant against quantum computers by design.
Basically, don’t panic just yet. Quantum computing isn’t quite there yet to threaten Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies security. And, research, development and proposals are already taking place in preperation for when quantum computing does become a threat.